Online Banking Insights
Your go-to source for the latest news and trends in online finance and banking.
Fair is Fair: Decoding Smart Contract Equity
Unlock the secrets of smart contract equity! Discover how fairness redefines the blockchain landscape and empowers your investments.
What Are Smart Contracts and How Do They Ensure Fairness?
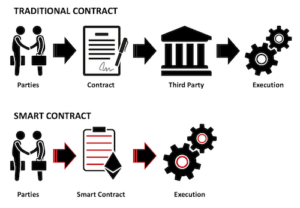
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They run on blockchain technology, which ensures that all transactions are transparent, tamper-proof, and irreversible. When predetermined conditions are met, the contract automatically executes the agreed terms without the need for intermediaries. This automation reduces the possibility of disputes and enhances the reliability of transactions by eliminating human error. Moreover, the decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that no single party has control over the contract, which increases trust among participants.
One of the key advantages of smart contracts is their ability to ensure fairness in various applications. For instance, in supply chain management, smart contracts can automate payments based on verified delivery of goods, ensuring that suppliers are paid timely and fairly. Additionally, in the context of financial transactions, smart contracts can facilitate peer-to-peer lending or insurance claims, where funds are only released when specific conditions are validated. This reduces the risk of fraud and fosters a sense of security among users, as they can rely on the contract's programmed rules instead of trusting a third party.
Counter-Strike is a popular first-person shooter game that emphasizes team-based gameplay and strategy. Players join either the terrorist or counter-terrorist side, engaging in various missions and objectives. To enhance your gaming experience, consider using a bc.game promo code for exclusive benefits and rewards.
Decoding Equity in Smart Contracts: Key Concepts Explained
Equity in smart contracts represents a crucial concept in the evolving landscape of blockchain technology. As these contracts enable self-executing agreements that are coded into the blockchain, understanding how equity is distributed among parties is paramount. At its core, equity refers to the ownership or stake that each participant has in a particular blockchain project or contractual agreement. This can involve various forms, such as tokens or shares, that signify an individual's claim to a portion of the assets or profits generated by the contract. In essence, equity ensures a fair distribution of benefits, providing a level of transparency and accountability that traditional legal agreements often lack.
One of the key considerations in decoding equity in smart contracts is the concept of decentralization. Unlike traditional contracts, which may involve intermediaries, smart contracts are designed to operate on a decentralized network, thereby eliminating the need for third-party oversight. This leads to a more direct relationship between parties involved and can enhance trust and efficiency. Additionally, it is essential to grasp how factors such as governance, valuation, and liquidity influence equity distributions. Understanding these elements will empower users to navigate the complexities inherent in smart contracts and leverage them effectively for equitable outcomes.
Are Smart Contracts Truly Fair? Debunking Common Myths
Are smart contracts truly fair? This question has gained traction as blockchain technology becomes more integrated into various sectors. At their core, smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. While they offer impressive benefits, such as transparency and automation, some myths persist regarding their fairness. One common misconception is that because smart contracts are automated, they eliminate the potential for human bias. However, the fairness of a smart contract is largely dependent on how the contract's code is written and the underlying logic. If the code is programmed with inherent biases or errors, the outcomes can be anything but fair.
Another prevalent myth is that smart contracts operate in a completely decentralized environment, free from regulation and oversight. In reality, the deployment and execution of smart contracts often rely on underlying blockchain protocols, which can have their own governance rules. Additionally, smart contracts are only as trustworthy as the data they rely on. If the information inputted into the blockchain is flawed or manipulated, the resulting contract execution could lead to unfair outcomes. Thus, while smart contracts provide opportunities for enhanced efficiency and reduced costs, they are not an infallible solution for equity in contractual agreements.